Beetle Dissection
Open the virtual beetle dissection here: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/sites/default/files/games/beetle-dissection/play.html
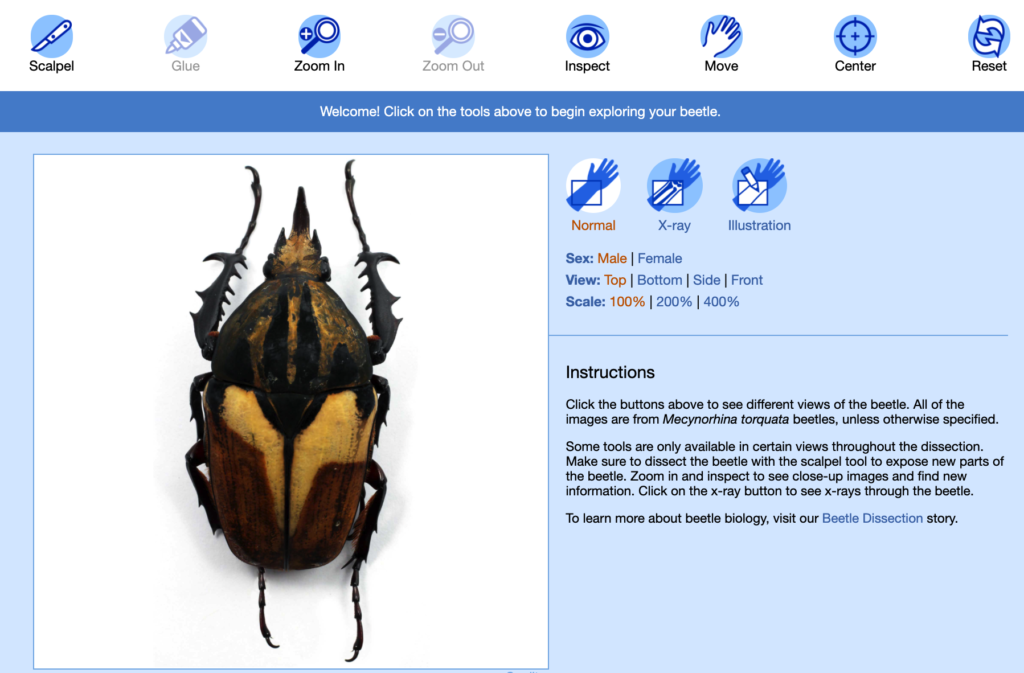
Dissect and inspect the male and female Mecynorrhina torquata beetles. While exploring, answer the following questions. If an answer is not available in the dissection tool, explore the website for the information you need.
Dissection Observations
- Record your observations of the following tissues and structures using the virtual dissection.
- flight muscles
- leg muscles
- brain
- eyes
- heart
- digestive tract
- testes
- eggs
- penis
- legs
- wings
- elytra
- spiracles
- air sacs
- fat body
- The form of an organism’s parts (what they look and feel like, how they’re shaped) often directly determines the function of that part. Choose three of the parts observed above and explain how the form of the body parts relate to their function.
- Which external structures are different between the male and female beetles? How are they different?
- Which internal structures are different between the male and female beetles? How are they different?
- Propose a reason why these internal and external structures are different between males and females.
- In many animals, females prefer males with certain traits. Might any of the traits you observe on the male beetle be related to female preference?
Exoskeletal System
- Look at the beetle’s elytra and wings. Which parts are used for flying? Which are used for protection?
- The beetle has hairs in many places on the outside of its body. What are these hairs used for?
- True or False: The elytra cover the wings, which attach to the abdomen.
- Where are the soft parts and the hard parts of the beetle’s exoskeleton? Why do they have both soft and hard parts?
Sensory Systems
- What are compound eyes?
- What is a ganglion? How many do beetles have?
- Examine the beetle brain. What are three main regions of the brain? What do they do? What sensory organs do they receive information from?
Respiratory System
- What are the parts of the beetle respiratory system?
- Why are there tracheae and air sacs throughout the flight muscles and leg muscles?
- How is oxygen transport different in beetles and humans?
- Propose a reason why these beetles have so many air sacs and why they are different sizes.
Muscular System
- How do beetles use muscles to move their legs?
- How do beetles use muscles to move their wings up and down?
- The dorso-longitudinal muscles do not attach to the wings, yet when the muscles contract, they depress the wings. How does this work?
Circulatory System
- Blood is called hemolymph in insects. Do you see any hemolymph in the virtual beetle dissection? Use an outside reference to discuss how insect blood and human blood differ.
- Some organs are used for many functions. What are the roles of fat body in the beetle body?
Digestive System
- Examine the beetle’s mouthparts closely. What kind of food might the beetle eat using these mouthparts?
- Use an outside reference to discuss how the digestive tract of the beetles differs from the human digestive tract.
- What is the function of Malpighian tubules? What human organ are they most similar to?
Putting it all Together
- Choose one of the body systems listed above. Explain how each of its parts work together as a system in the beetle.
- How and why is this system different in humans?
- What would happen to the beetle if this system was removed?
Post-Dissection Activity
Refer to your “Build A Beetle: Pre-Dissection Activity” beetle drawing. With your new knowledge of beetle anatomy, answer the following questions:
- What parts did you add to your beetle drawing that the beetle dissection did not have? Why did you add them?
- Did you think the parts you mentioned in question 1 were important? Do other parts of the beetle perform the functions these parts would have performed? If yes, how?
- What parts did you leave out of your beetle drawing that were in the beetle dissection?
- Why are these parts important for the beetle to function?
- You probably drew many of the same parts that you saw in the beetle dissection. Pick one that looks different than you expected. What did you expect this part to look like? How does the appearance of this part in the beetle dissection relate to its function in the beetle?
For 5 points of extra credit, you can work through the Beetle X-ray activity on the Beetle Dissection site. Download the worksheet below, and then work through the activity here: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/micro-ct-beetle-navigator. Upload your completed worksheet to the Extra Credit assignment in Canvas. (You may submit multiple files to that assignment, so don’t worry if you’ve already submitted any extra credit activities).