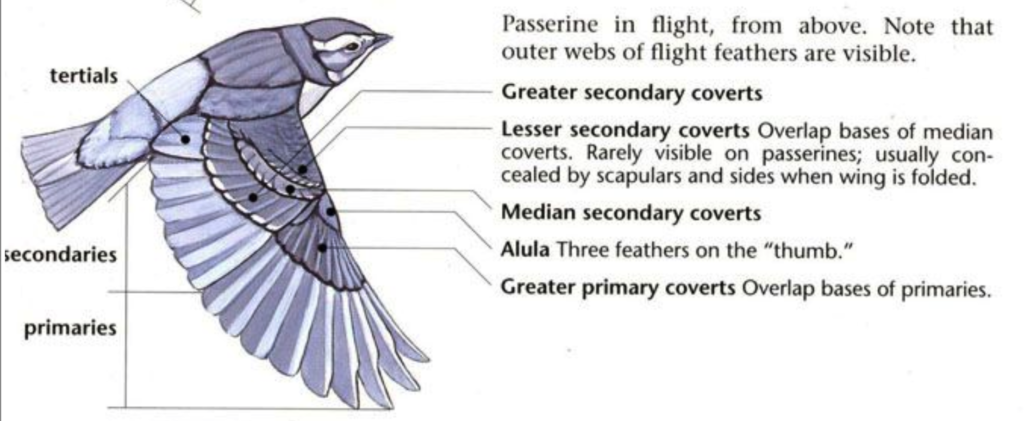
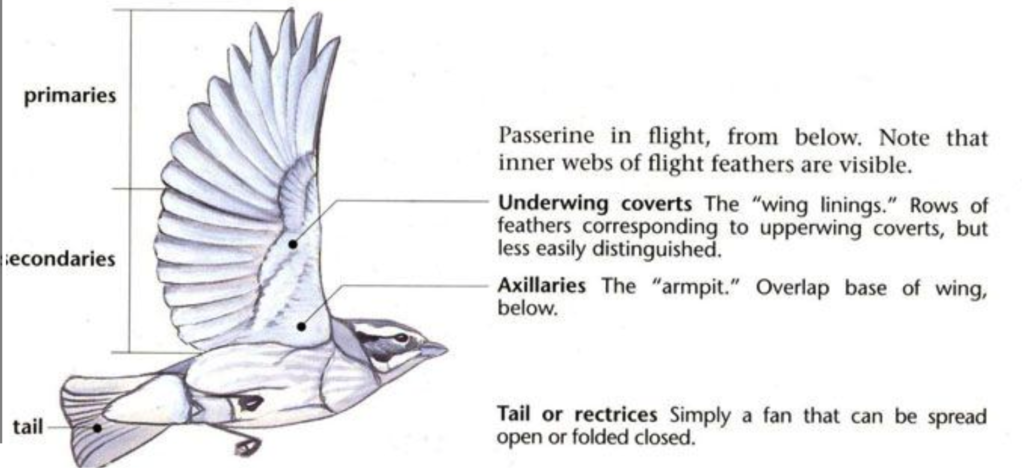
Visit this website to explore the structure of feathers:
https://academy.allaboutbirds.org/features/all-about-feathers/#how-feathers-are-built.php
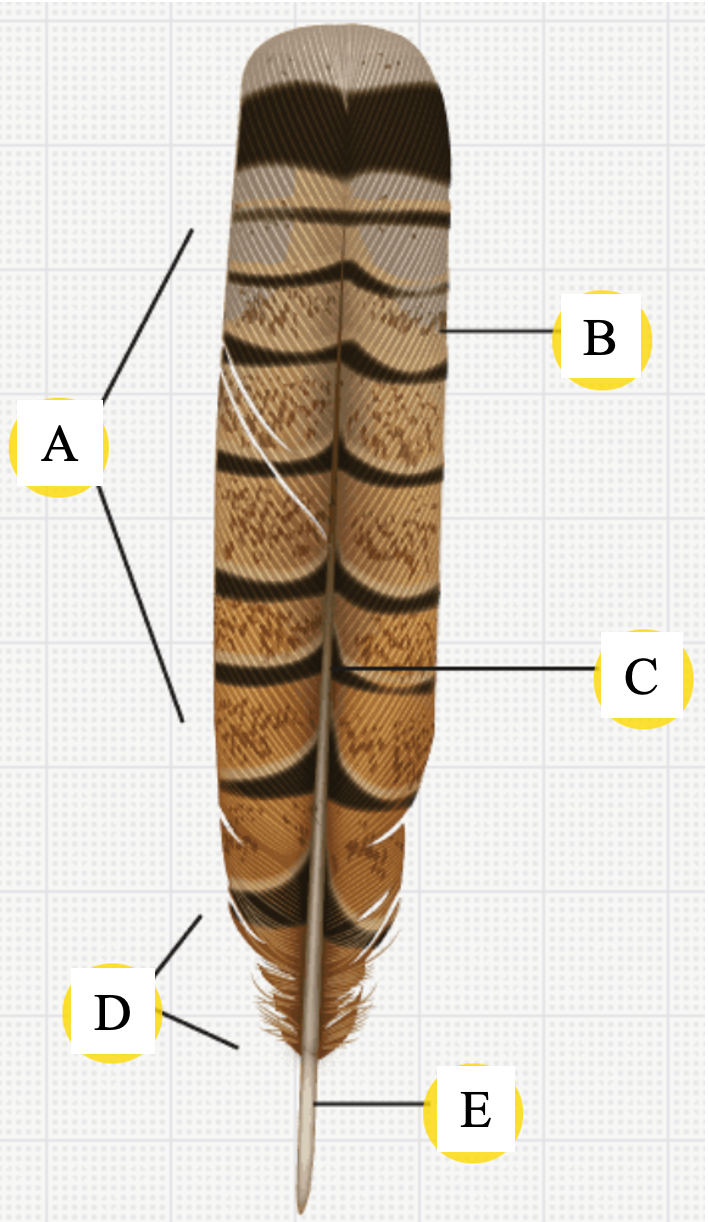
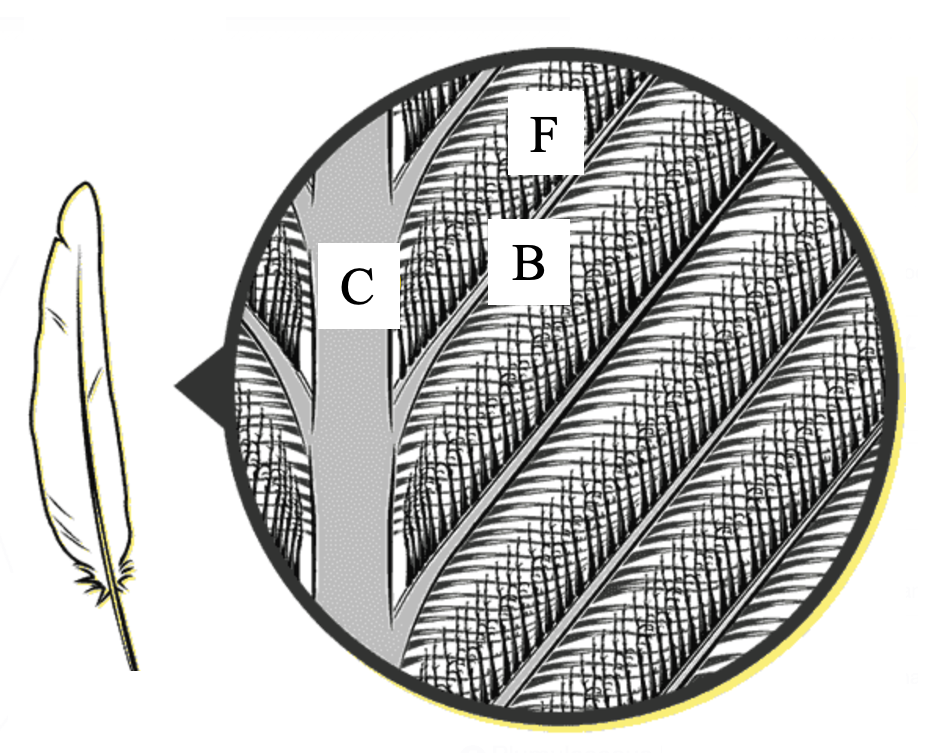
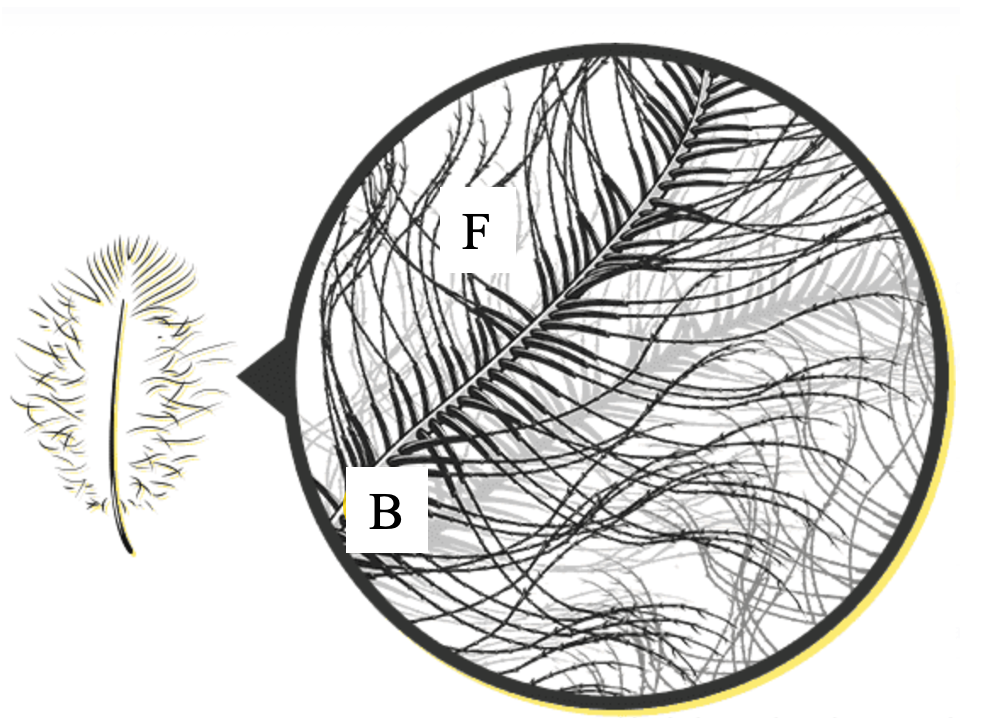
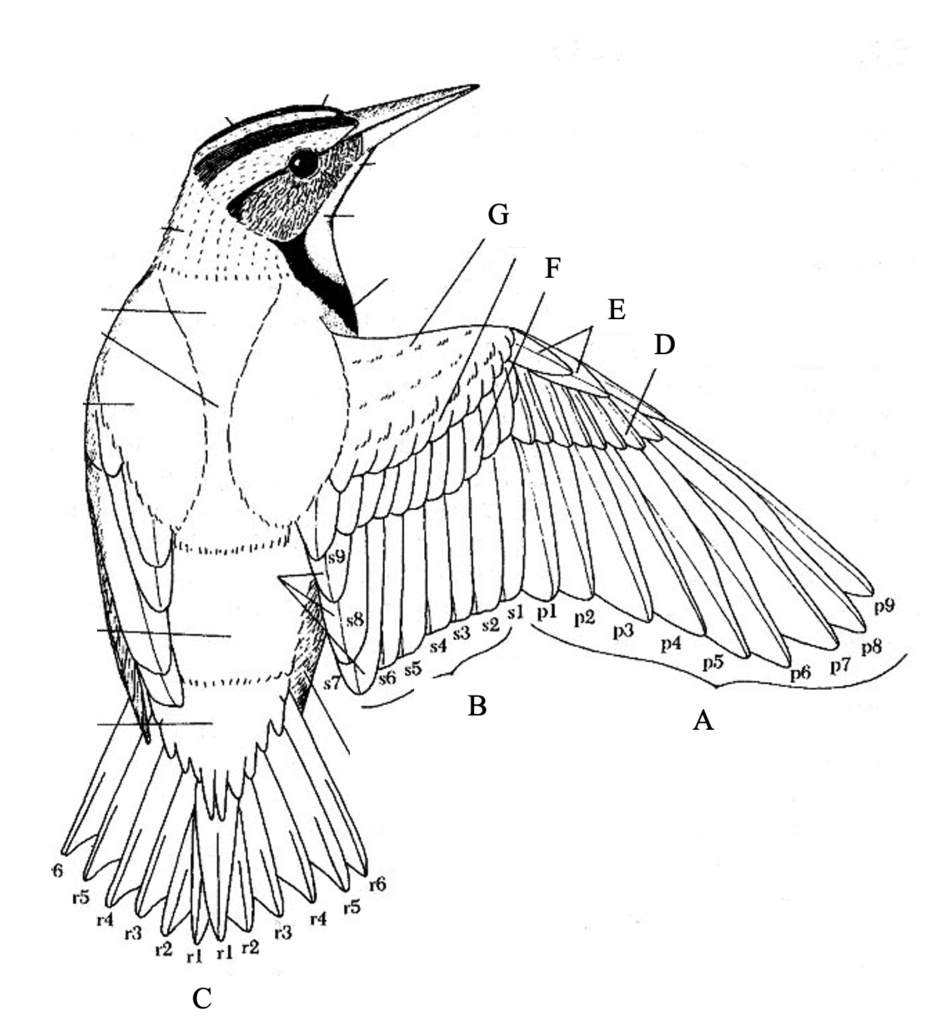
- On the illustrations below, match the letters with the correct structures:
- Group of answer choices
- Calamus
- Rachis
- Vane/Pennaceous Region
- Barbs
- Plumulaceous Region
- Barbules
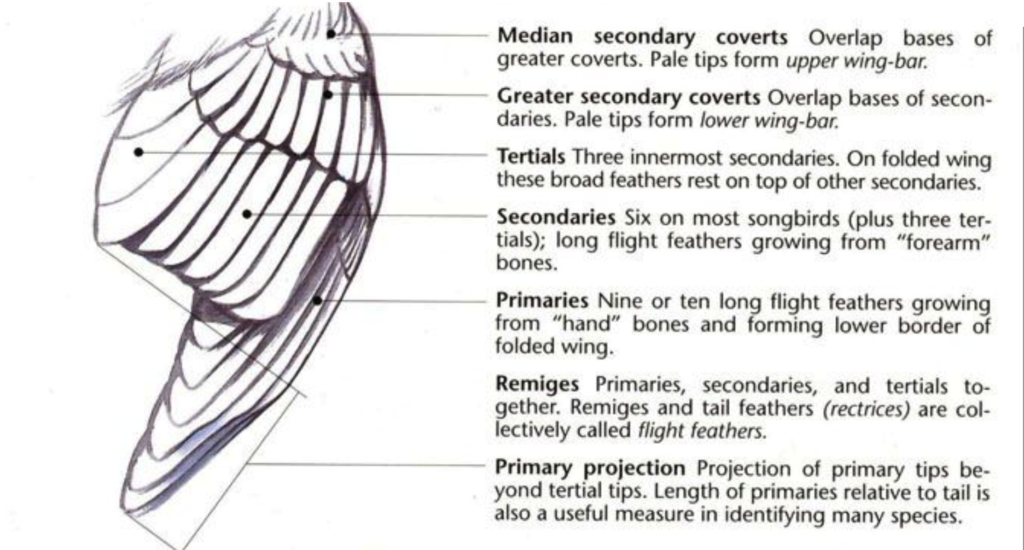
2. Use the information below to correctly identify the location of various feather types on the unlabeled diagram.
- Group of answer choices
- Primaries
- Secondaries
- Rectrices
- Primary coverts
- Alula
- Greater coverts
- Lesser coverts
Visit this website, and read about the structure and function of each of the following feather types: https://academy.allaboutbirds.org/feathers-article/.

Use information from that website to answer the following questions.
3a) What is the primary function of Down feathers?
3b) What is it about their structure that allows them to serve the function above?
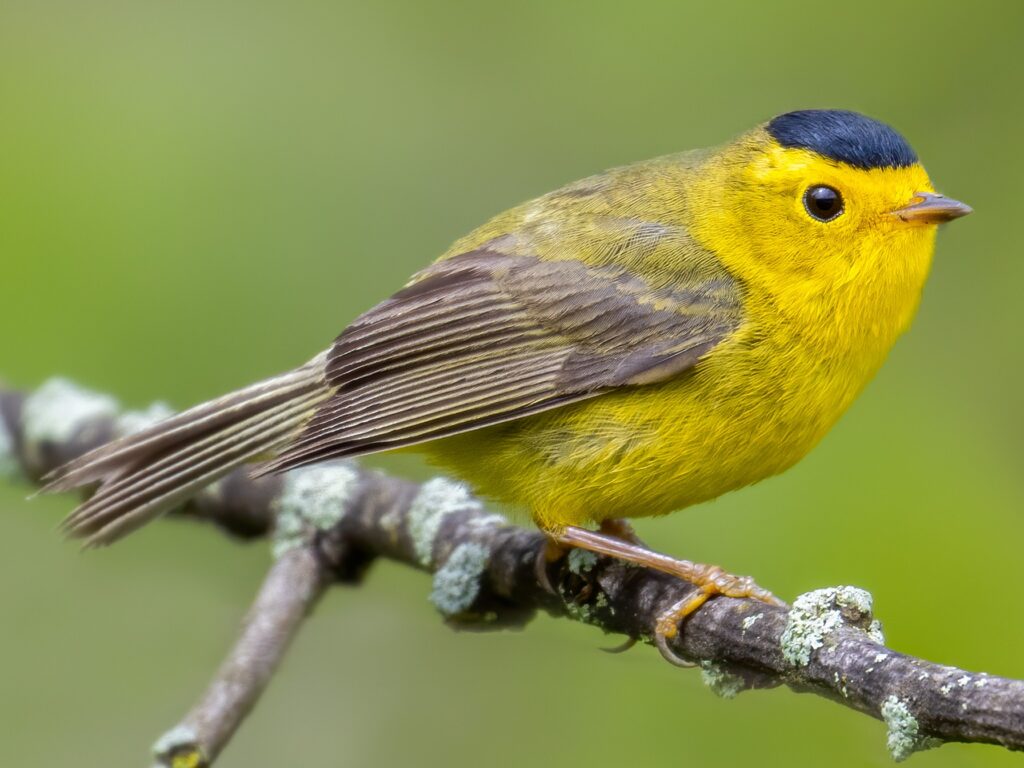
4, Consider the feathers on the head of the bird pictured below. Why have bristles rather than regular vaned feathers located here?

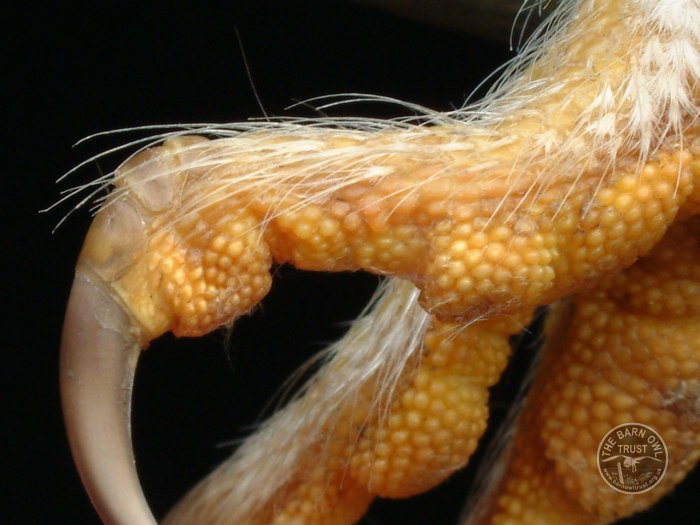
5. Look for feet bristles on the owl pictured below. What purpose do these feathers serve?

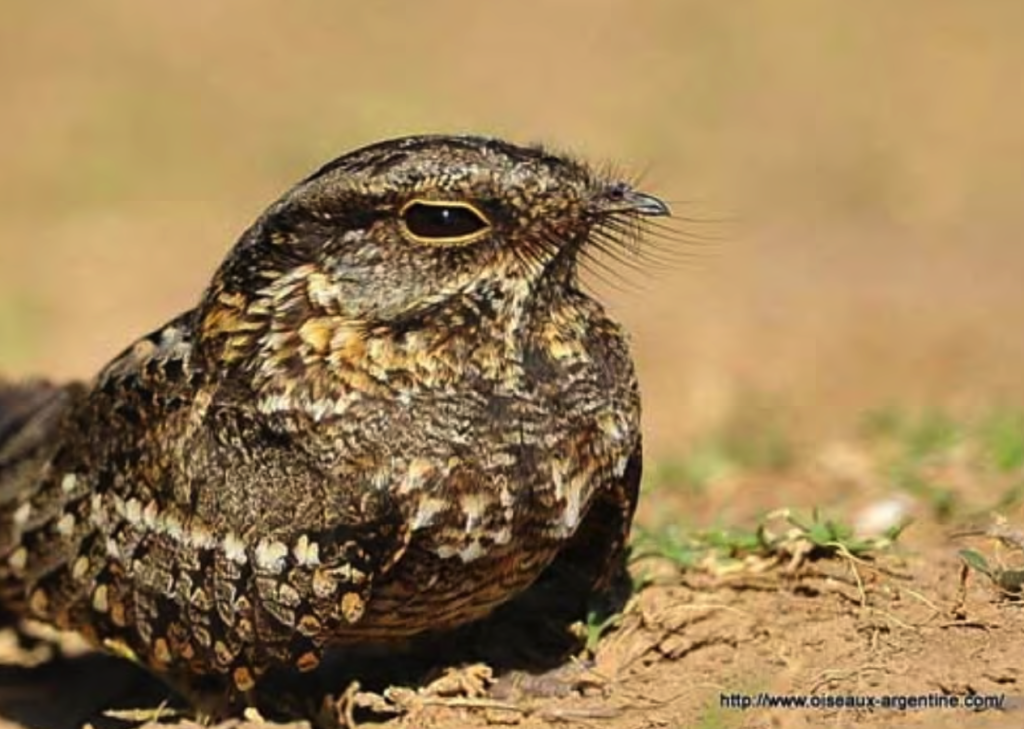
6. Look at the facial bristles on the Nighthawk. Name two functions of these feathers.

7. Look at the tail bristles on the swift.
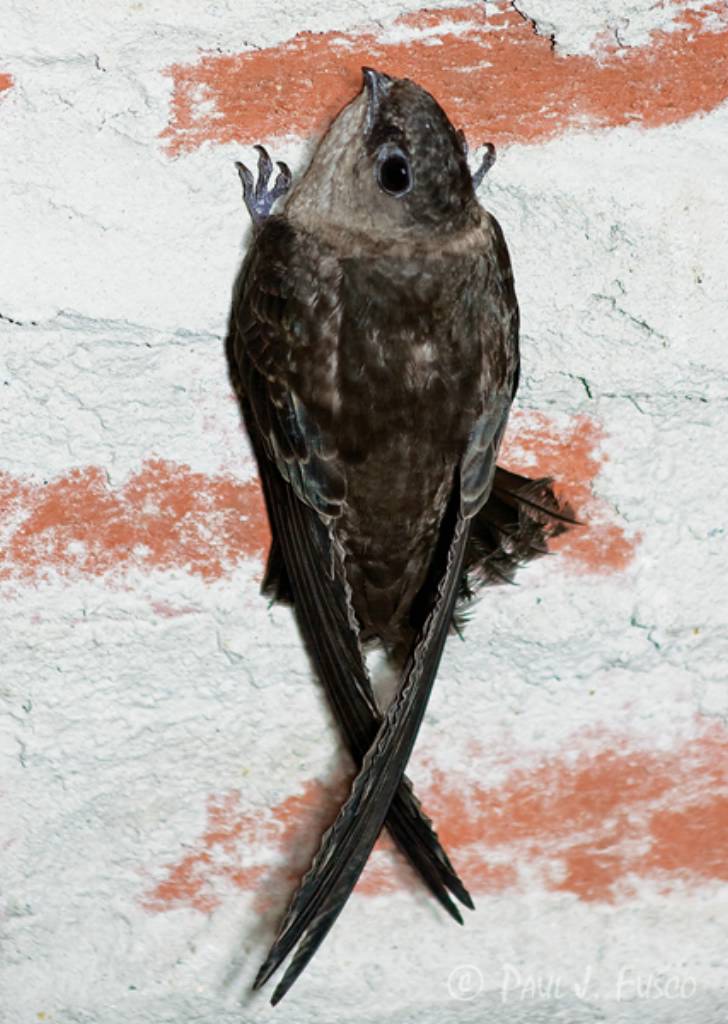

a) What purpose do you hypothesize that these feathers serve?
b) Do whatever outside research is necessary to find the answer to that question, and provide a summary of their function.
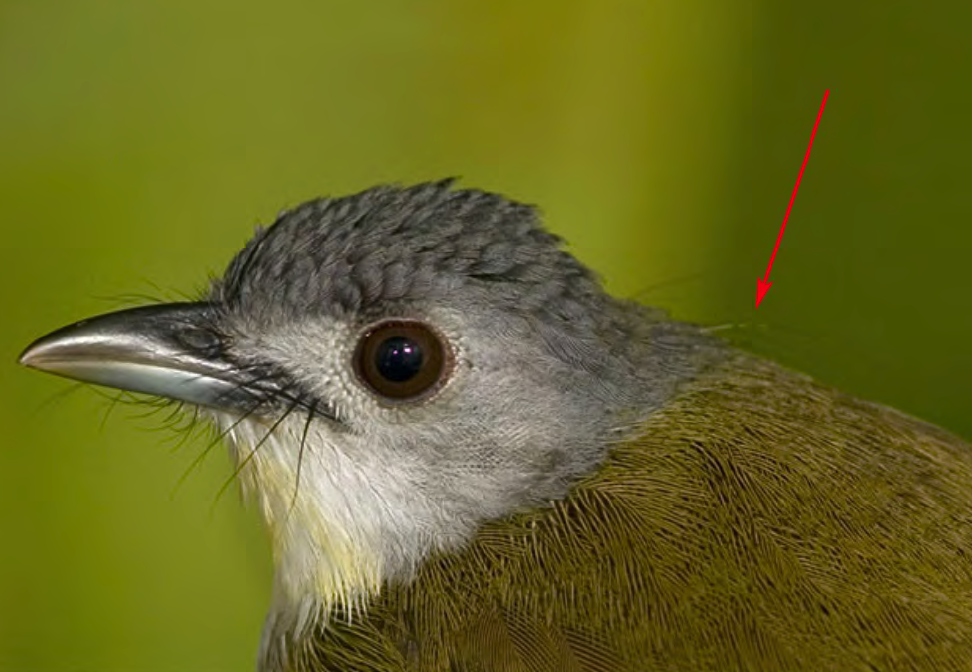

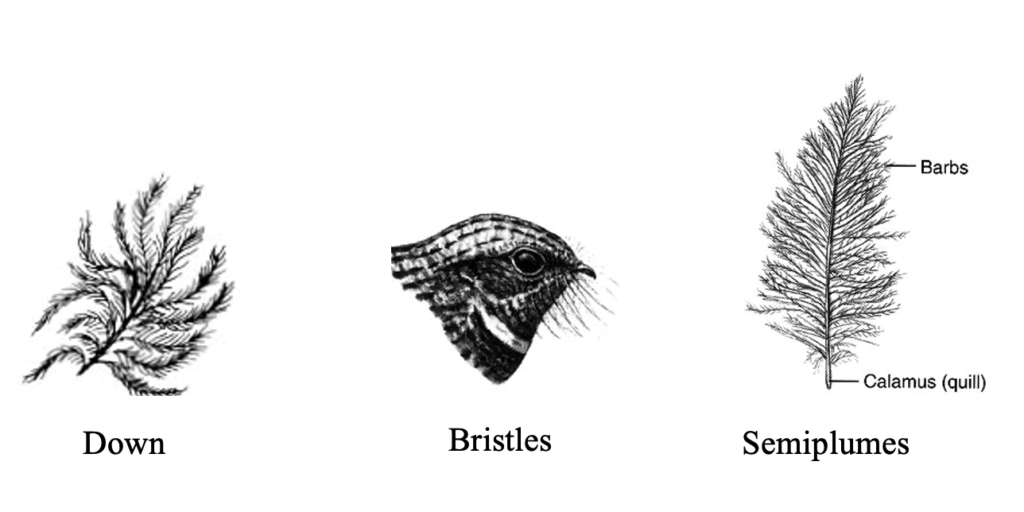
8a) What purpose do the filoplumes serve?
8b) Describe their general morphology
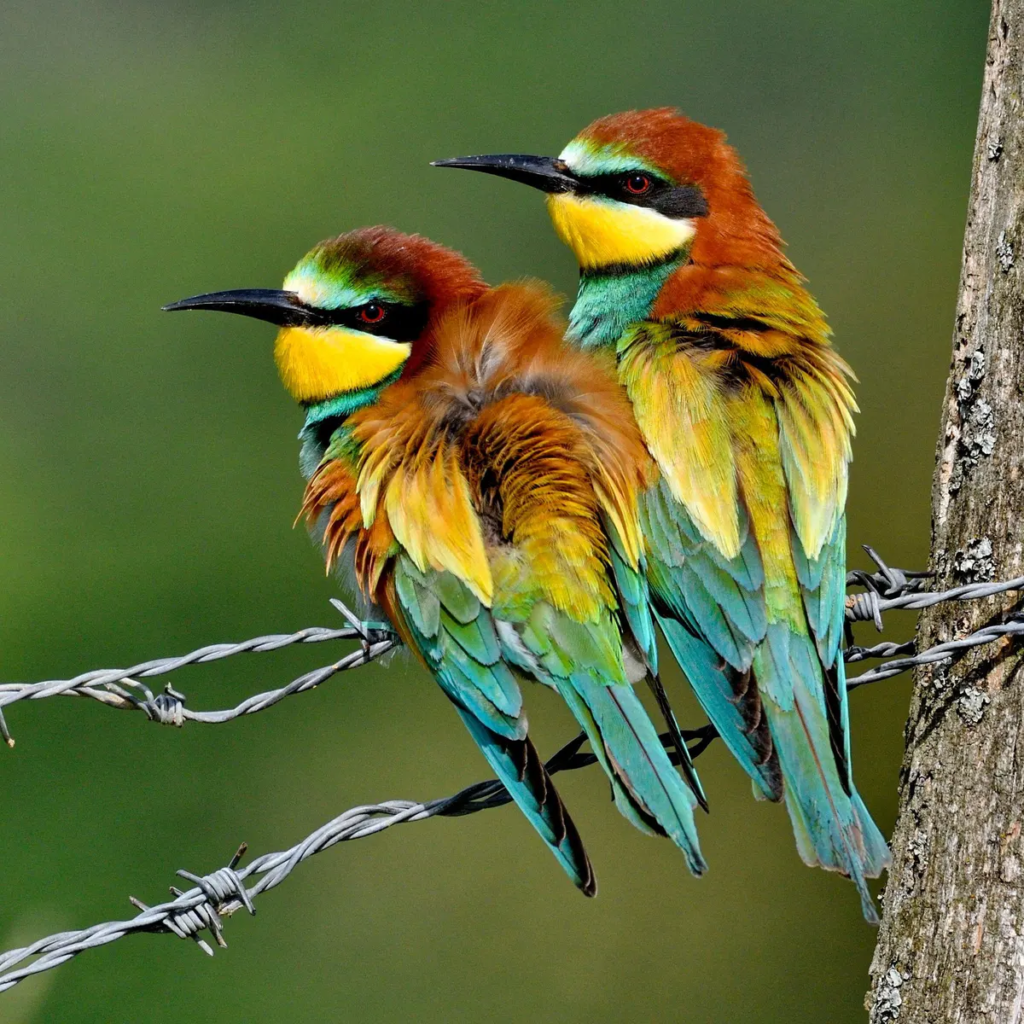
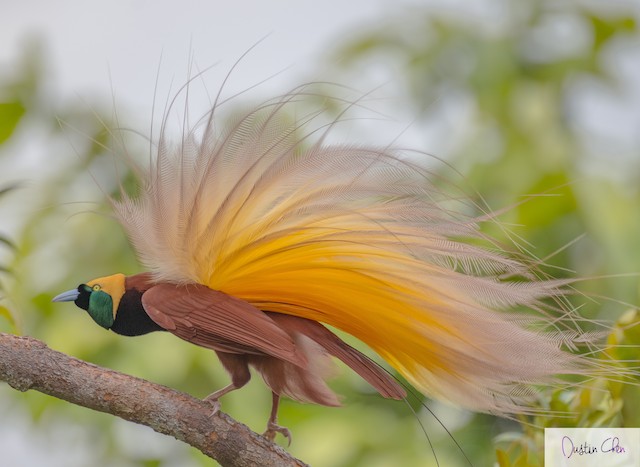
9. Note elaborate rectrices on the birds pictured below. What function do these elaborations serve?
10. Describe any feather adaptations that might be associated with swimming in the bird featured in the video above.
11. What type of non-vaned feather are often used for courtship ornaments?

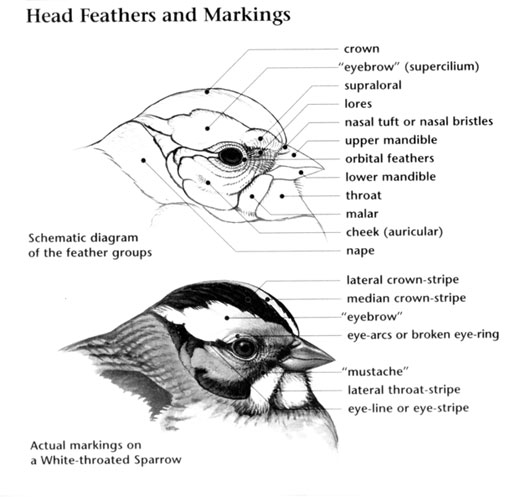
For the next three questions, use the diagram below to help identify the head markings on the birds pictured. For each bird, submit a description of these markings, as for a field notebook entry, that one would use to distinguish the species.
15. We know that aspect ratio of the wing is a key indicator of flight performance characteristics. Here is a good resource with more information: http://www.pelagicos.net/MARS4040_6040/labs/Mars4040_6040_Fa16_Lab_WingMorphology.pdf
a) Take approximate, relative measurements of Maximum wing width and Maximum wing length on the specimens pictured above. (You could hold a ruler up to the computer screen – it’s fine if your measurements aren’t life-sized, as long as the ratio is accurate).
Specimen 1 width:
Specimen 1 length:
Specimen 2 width:
Specimen 2 length:
b) Using the values you estimated, calculate aspect ratio and identify which bird has higher aspect ratio.
c) What does this probably mean regarding the flight performance of these species?
Specimen 1:
Specimen 2:
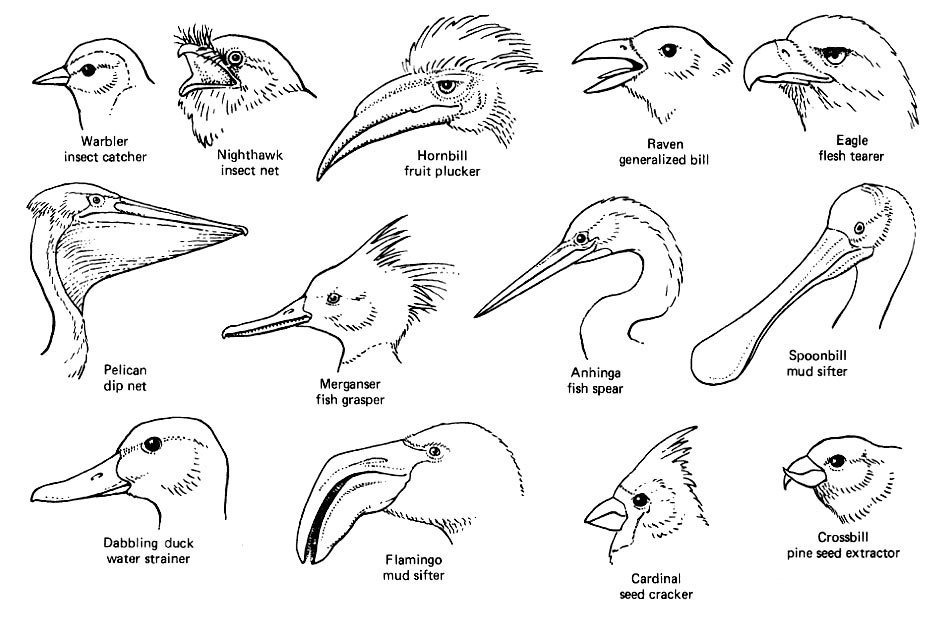
16. Using the diagram above, determine the mode of feeding/type of food preferred by each of the birds pictured below. if possible, identify the species, as well. (If you are not able to get to species, it is fine to list the order).
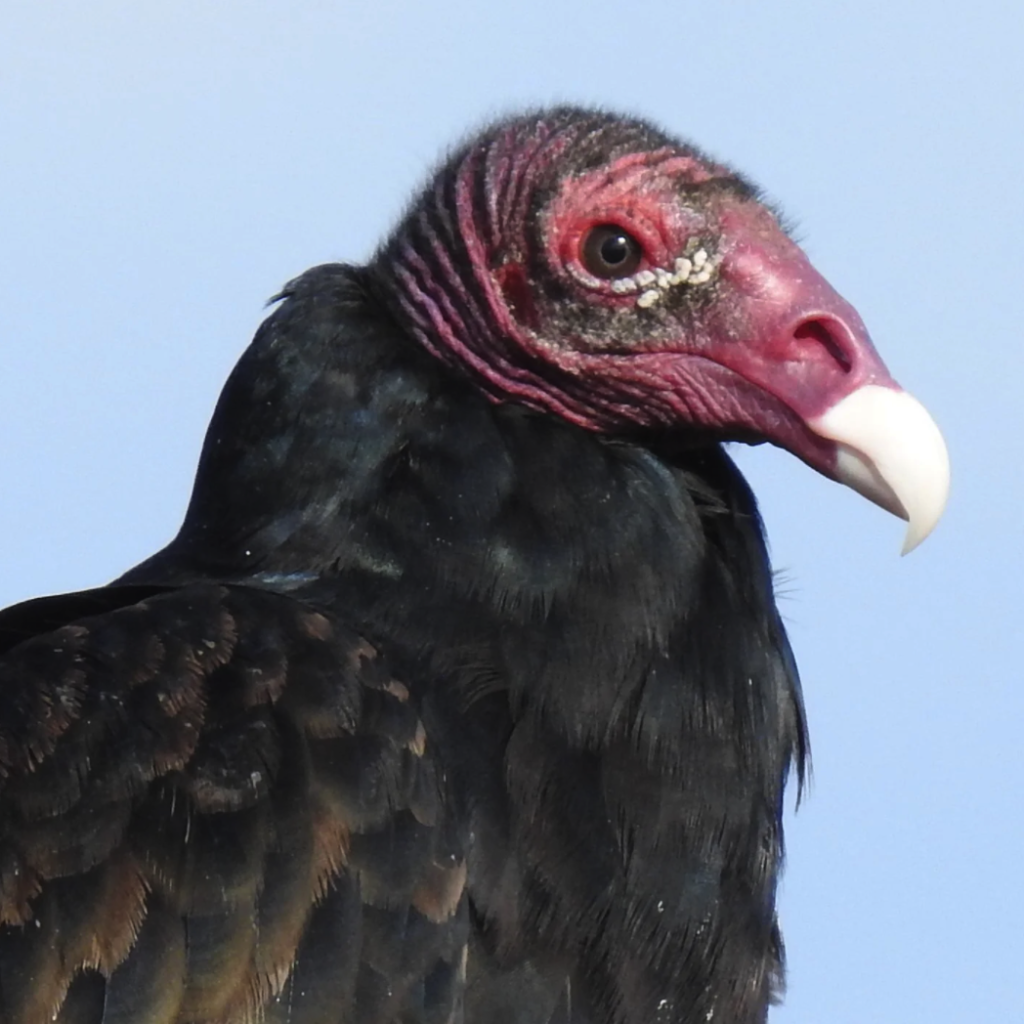
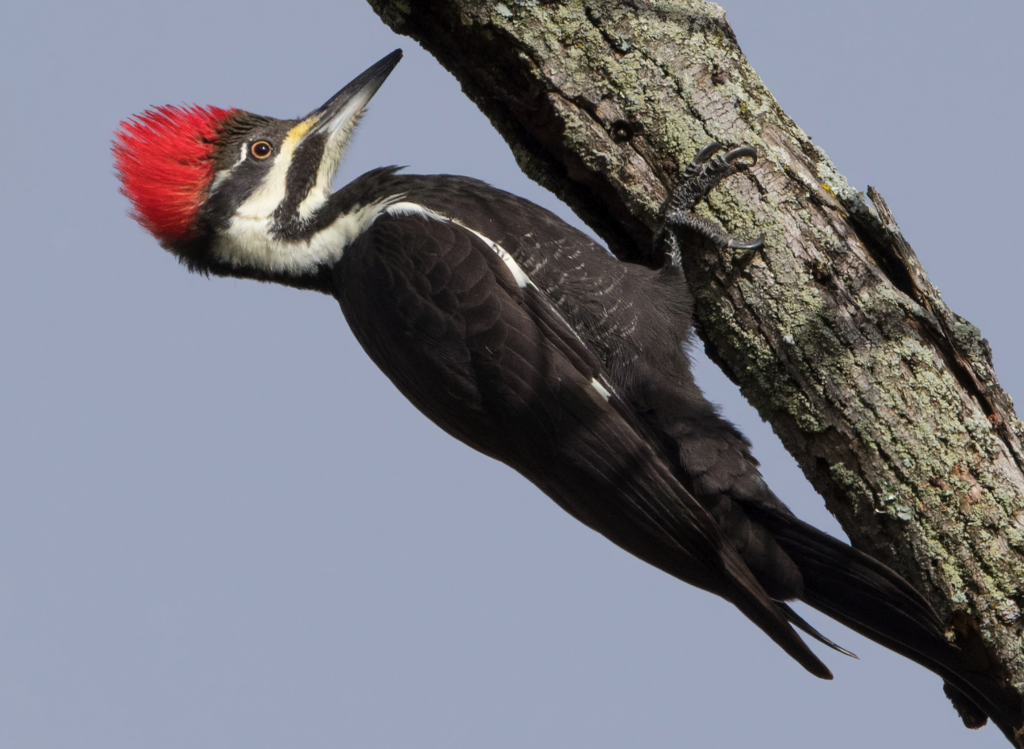
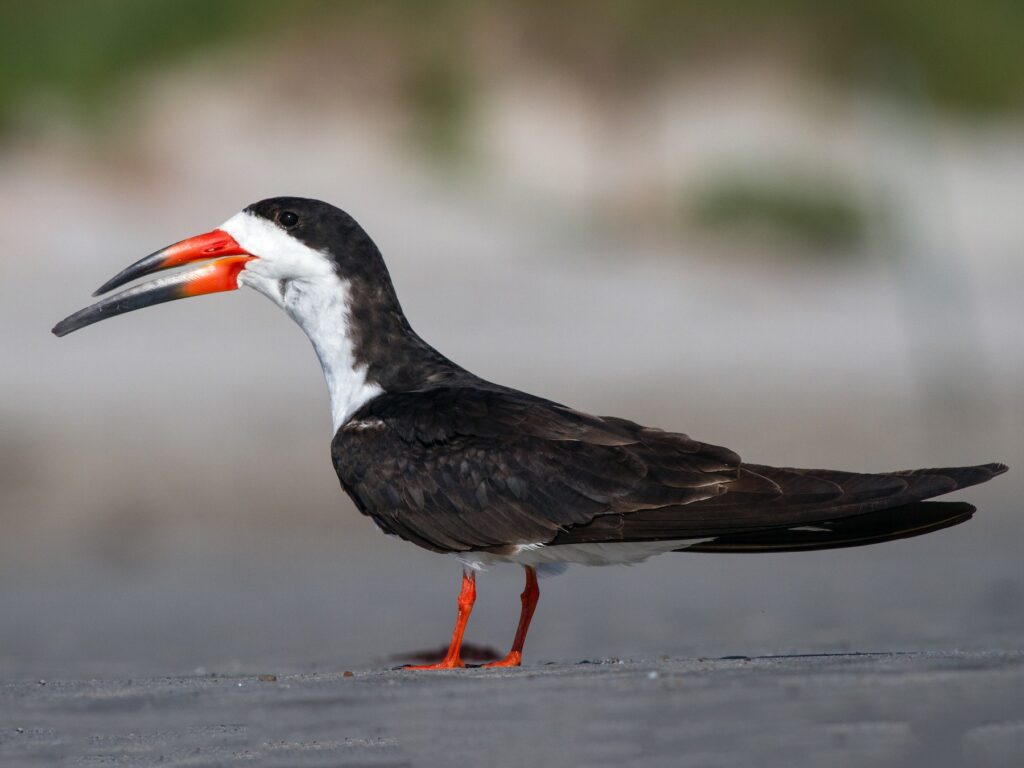
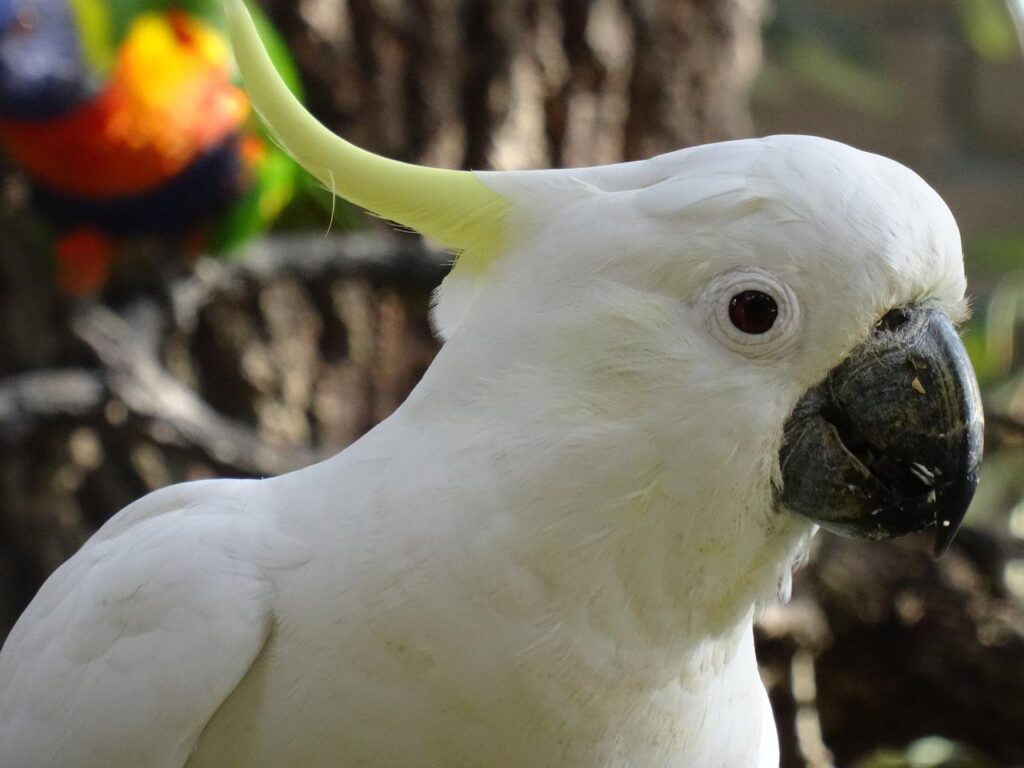
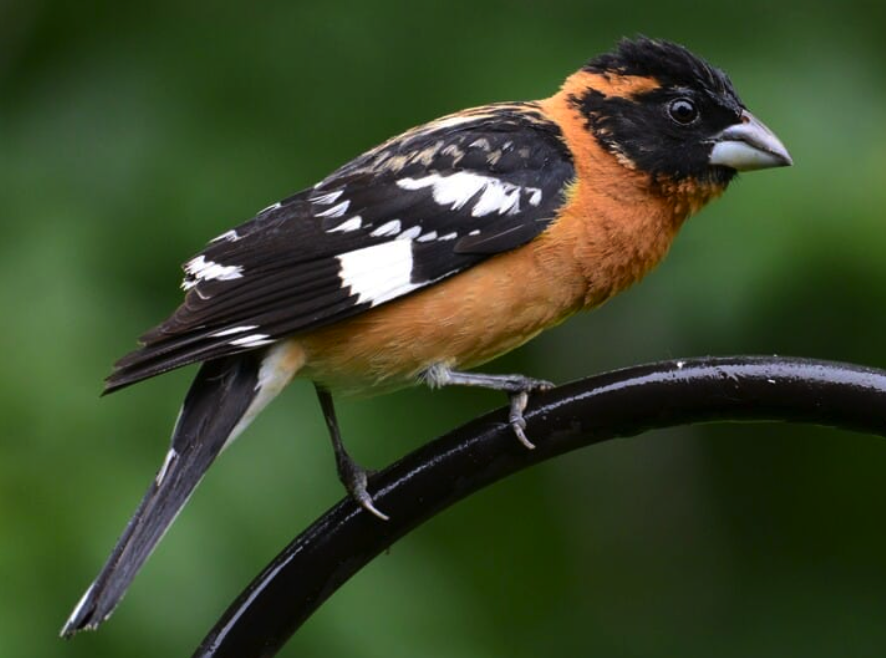
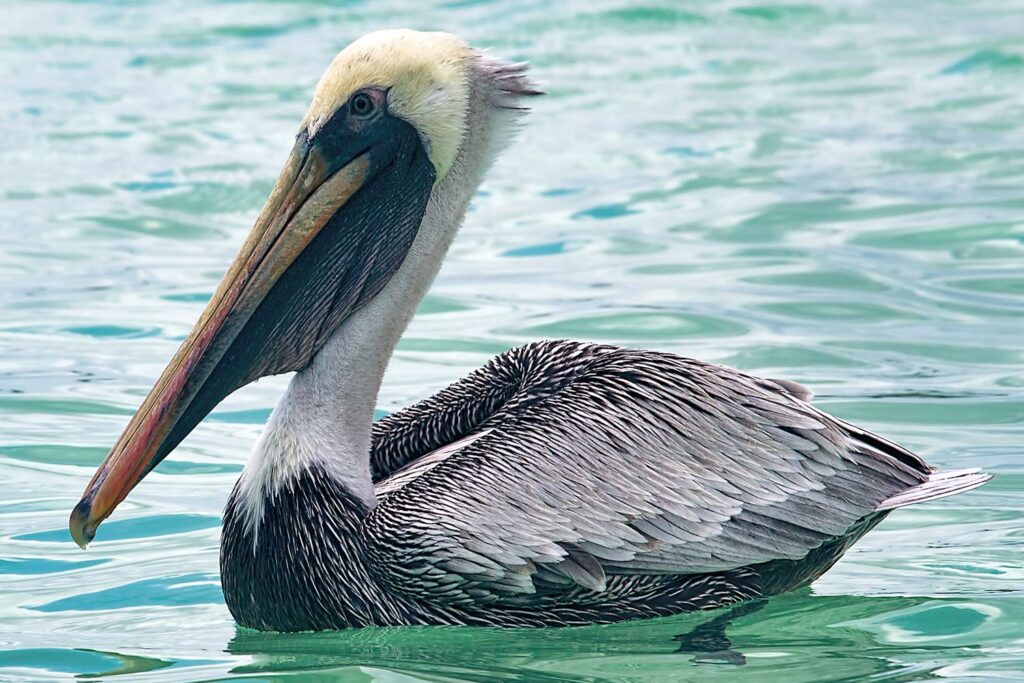










1
17. Consider Anna’s hummingbird (Calypte anna) and Violet Sabrewing (Campylopterus hemileucurus). Why might these bills be different yet use a similar feeding strategy?
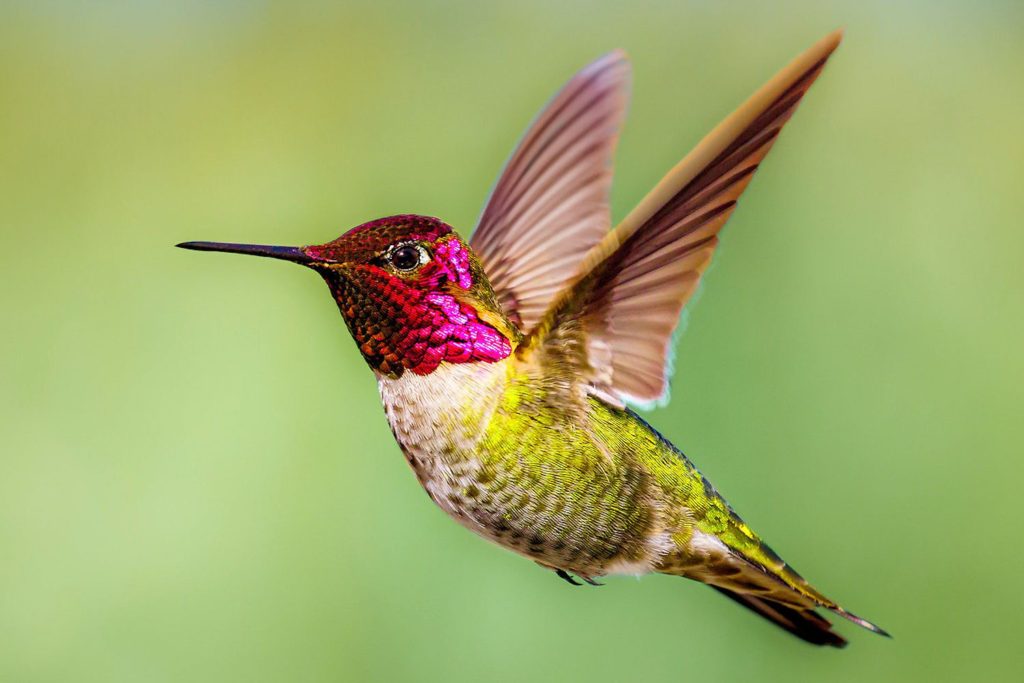

Anna’s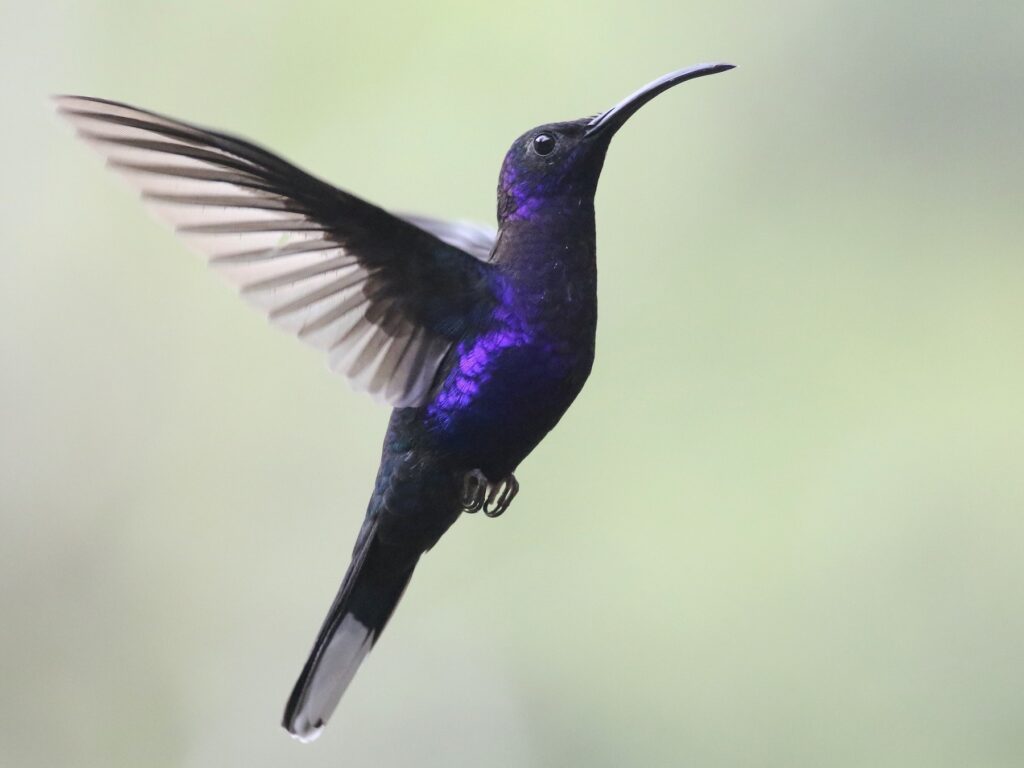 
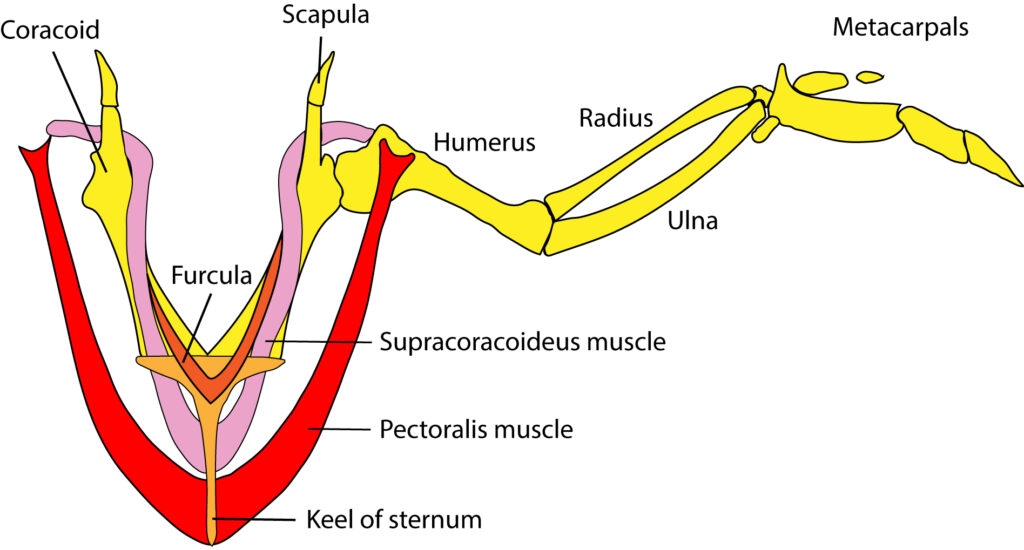
Consider the skeletal structures pictured below to answer the remaining questions. This website also has information that will be useful in answering the questions: https://brianmccauley.net/bio-6a/bio-6a-lab/chordates/bird-skeletons
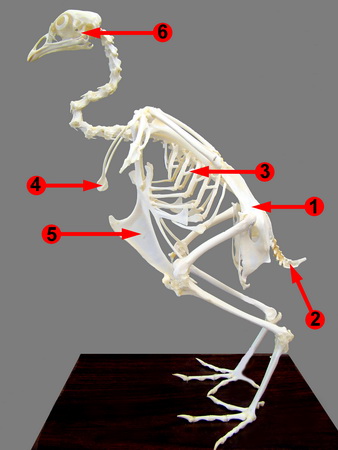
- Synsacrum
- Pygostyle
- Uncinate processes
- Furcula
- Keeled sternum
- Quadrate bone
18a) Identify as many skeletal structures as possible that are adaptations for flight.
18b) What adaptations have been made to the beaks of birds to aid in flight?
19a) Where does the furcula articulate with the rest of the skeleton?
19b) What role does it play?
20. Identify and find major regions of fused vertebrae.
a) Name these structures.
b) Why are they in this condition?
Find examples of uncinates
c) describe their function
21. Identify the location of both the pectoral and supracoracoideus muscles.
a) Where does the supracoracoideus tendon attach to the humerus? Why?
b) How does this tendon interact with the shoulder joint? What role does this muscle play?
c) Where do the tendons for the pectoralis insert? What role does this muscle play?
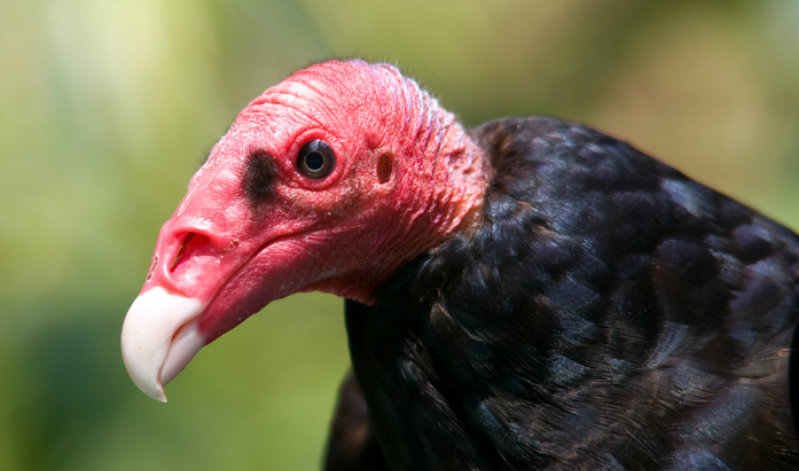
22. Examine the tips of the wings of the Turkey Vulture pictured below.
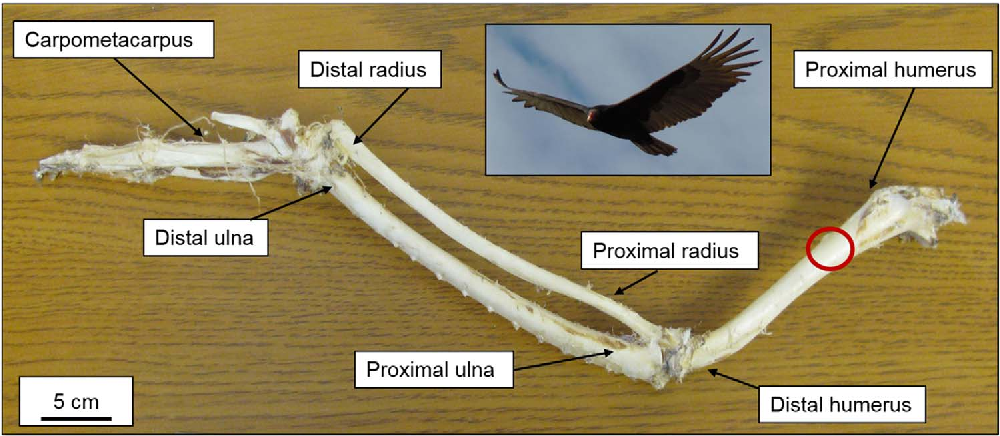
a) Describe which digits from your hand are represented in the bird wing.
b) Describe the developmental pattern of digit emergence in birds.